TPN 101: The Art of Electrolyte & Acid-Base Tuning
- ckhendry7
- Aug 12, 2025
- 1 min read

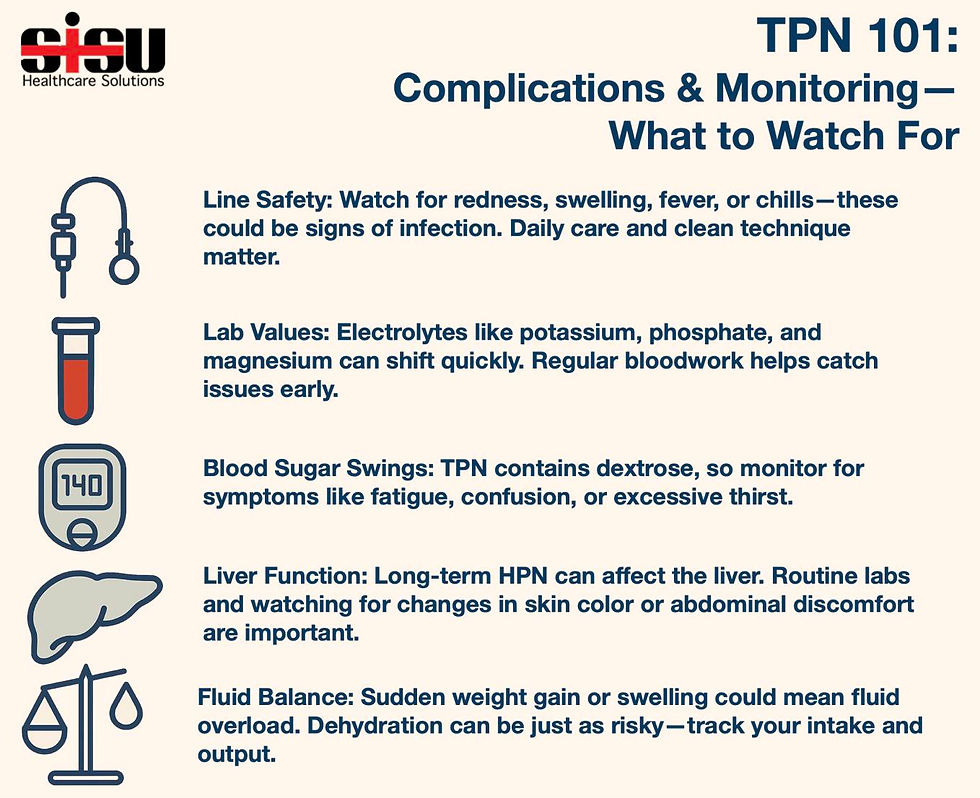
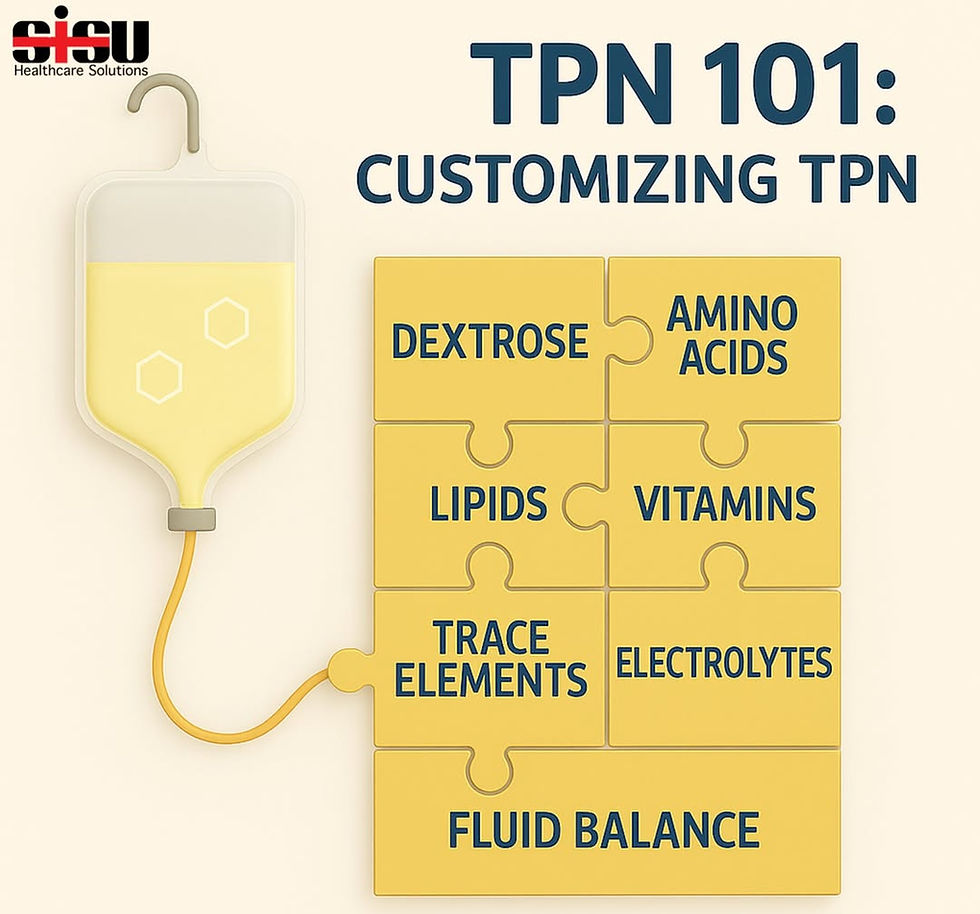
TPN isn’t just nutrition—it’s an intricate biochemical formula tailored to the body's every need. Here's why each electrolyte matters:
Sodium: Critical for fluid balance and nerve function. Too much? Risk of fluid overload. Too little? Confusion, cramps, and hypotension.
Potassium: Vital for muscle contractions, especially the heart. Precision is everything—small shifts can have big consequences.
Chloride: Influences acid-base status via strong ion difference. Elevation may drive acidosis; depletion affects buffering.
Magnesium: Supports enzyme systems and neuromuscular function. Often overlooked, but low levels can derail recovery.
Calcium: Key to neuromuscular stability and blood clotting. TPN dosing demands careful coordination with phosphate to prevent dangerous precipitation.
Phosphate: Backbone of cellular energy and structure. Inadequate levels impair tissue repair, while excess can disrupt calcium balance.
Acetate: Converted to bicarbonate, it’s your buffer against metabolic acidosis when lactate isn’t used.
Each component is a dial we adjust to meet complex clinical needs.

Comments